General
The Tail Assignment Optimizer in N-OC Desktop is a tool used to assign flights to aircraft, either using simple assignment principles like ‘first in first out’/’last in first out’, or by optimization.
There are several different predefined objectives the optimizer can work towards. For example, to make the aircraft follow the crew pairings, or to reduce unnecessary ground time for aircraft.
The tool can be used, either to move flights from ‘ghost’ aircraft to real ones, or to move around flights already assigned to aircraft in order to find a better solution.
The Optimizer can be set to follow, or ignore onward references, and multi leg flights.
Options for maintenance can be set so that the provided solution from the tail assignment optimizer makes room for maintenance checks after a specified number of days, flight hours, or landings.
Note: The Optimizer requires that VcRedist64 (2015-2019) is installed on the PC.
https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/help/2977003/the-latest-supported-visual-c-downloads

When you click the Wizard icon in the Schedule Gantt, the window opens. To get to the Tail Assignment Optimizer, click the first icon in this window, titled 'Tail Assign Optimizer'.
Load Data
The next screen concerns loading of data.
Flights and aircraft can be loaded directly from the database by selecting the Load radio button, and entering the start and end of the desired period in the fields at the top of the window.
Alternatively, the data already loaded in the Schedule Gantt can be used by the Tail Assignment Optimizer. For this option, select the Gantt radio button option in the as in the above image.
Clicking the Next button will take you to the main window of the Tail Assignment Optimizer.
Note: The Gantt option loads the zoomed period, and the time is UTC.
Main window of the Tail Assignment Optimizer
This page contains general settings which apply to all optimization algorithms.
Left Side of the Window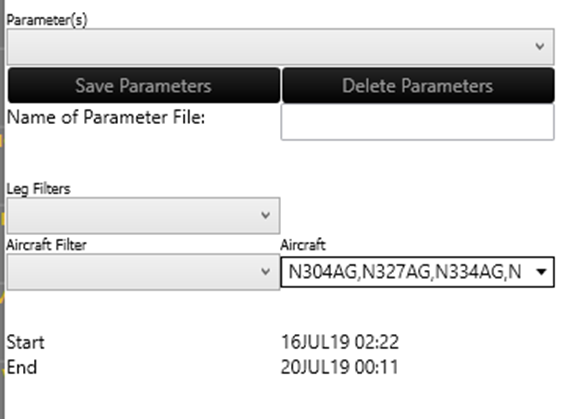
Field | Description |
| Parameter templates | The saved parameter file. To load an already saved parameter template, select it in the dropdown. |
| Leg Filters | Select a Leg Filter from the dropdown list. |
| Aircraft Filter | Select an Aircraft Filter from the dropdown list. |
| Aircraft | Individual aircraft can be selected. |
| Name of Parameter File | Enter a name of the template in Name of Parameter File: field then click the Save Parameters button. |
| Save Parameters | Save the parameters to the database. |
| Delete Parameters | To delete the selected parameter template, click the Delete Parameters button. |
Note: If in the previous step, loading data from Gantt was chosen, then only leg filters and aircraft filters containing flights and aircraft already loaded in the Gantt will be applicable. If no filters are selected in this window, all legs and aircraft currently loaded will be included in the optimization.
Lower Part of the Window
In the lower part of the window, all legs currently loaded into the system are displayed. Each row corresponds to a flight. 
Field | Description |
| Registration | What aircraft is currently assigned to fly the corresponding flight. |
| New Registration | This will be updated after the optimization is complete. It will then display which aircraft the flight is assigned to in the provided solution. |
| Run | Start up the Tail Assignment Optimizer with the chosen settings. |
| Save | Save the solution into the database. |
| Cancel | Cancel the ongoing run. |
After a run is complete, the solution will be displayed in the Schedule Gantt, but will not be saved until the Save button in the Tail Assignment Optimizer window is clicked.
Note: Saving results from the Tail Assignment Optimizer using the CTRL+S, or any other button in N-OC Desktop will not work, and that this button in the Tail Assignment Wizard must be used.
General Tab

Field | Description |
| Ignore Preassigned Maintenance | If checked, the preassigned maintenance will not be considered in the optimization run. If unchecked, the preassigned maintenance can be taken into consideration when using the ‘Column Generation’ rotation option. Note: When having Maintenance slots assigned to the aircraft, it sometimes happen that the Optimizer leave unassigned flights. To solve this problem use a high "Unassigned Flights Penalty". E.g. 100000. |
| Ignore Onward | Onward references will not be considered in the optimization run. Note: If a flight has an Onward reference, the Turnaround Table will be overruled. |
| Ignore Type | Vehicle types will not be considered in the optimization run, but flights will be allowed to be assigned to vehicles of any type. |
| Ignore Version | Vehicle versions will not be considered in the optimization run, but flights will be allowed to be assigned to vehicles of any version. |
| Ignore Locked Flights | Flights which has been marked with the “Lock to ac” tag are allowed to be assigned to any vehicle. Note: This option only apply to Column Generation. |
| Ignore Initial Positions | Previous stations for vehicles will be disregarded, and initial positions will be set for each vehicle as deemed most suitable by the algorithm. This is mainly needed if flights are loaded from a SSIM file, and no previous flights for aircraft are specified in advance. |
| Ignore End Stations | End stations for vehicles will be disregarded in the optimization run. Option to force end stations is to be used if flights are already assigned to aircraft, and the user wants to optimize/re-optimize a certain period within the schedule, leaving the later period untouched. |
| Use Estimated Times | Estimated times will be used for flights which has them. |
| Show Maintenance Possibilities | Maintenance is taken into consideration in the run. All maintenance possibilities which satisfy the set rules are displayed in the Gantt after a completed run. |
| Ignore Multileg Connections | Multileg connections will be allowed to be broken in the solution. |
| Ignore Aircraft Availability | LIFO/FIFO/Column Generation: For each day, if the aircraft is unavailable, no flight assignment is allowed for that day. Min Cost Flow: If the aircraft is unavailable on any day in the selected period, then don't allow any assignments to this aircraft. |
| Fixed Turn Around | The turnaround time specified in "Minimum Turn Around" will be used as the minimum allowed turn around time between any flights, for any vehicle. If not checked, turnaround rules specified in the N-OC system will be used. |
Rotation Options
Option | Description |
| LIFO | Last In First Out algorithm will be used. Using this, the last aircraft to land on an airport will also be the first one to leave that airport. Note: Maintenance constraints, locked flights, and preassigned maintenance cannot be used with this algorithm. |
| FIFO | First In First Out algorithm will be used. Using this, the first aircraft to land on an airport will also be the first one to leave that airport. Note: Maintenance constraints, locked flights, and preassigned maintenance cannot be used with this algorithm. |
| Min Cost Flow | Minimum Cost Flow optimization algorithm will be used. This means that the optimizer will find the (according to the selected objective function) cheapest combination of aircraft routes as the solution. Note: Maintenance constraints, locked flights, and preassigned maintenance cannot be used with this algorithm. |
| Column Generation | Column Generation algorithm will be used. This algorithm will start from a basic solution where all flights are cancelled then iteratively find the best aircraft route relative to the current solution, and add that one. Heuristics methods are also applied in order to fix good parts of the generated aircraft routes. Note: All constraints are taken into consideration when using this algorithm. |
Results Options
Options | Description |
| Objective Value | The objective value. |
| Runtime in minutes | The runtime in minutes appear. |
| Flight | The number of flights. |
| Ghosts | The number of Ghost aircraft. |
| Maintenance Acts | The number of maintenance activities. |
| Vehicles | The number of aircraft. |
| Unassigned Vehicles | The number of unassigned aircraft. |
Advanced Tab
This tab contains settings which affect the internal workings of the ‘min cost flow’ and ‘column generation’ algorithms.
Time Windows Tab
This tab contains settings for Time Windows used in the Column Generation algorithm.
Time windows are used to speed up the optimization, and is needed to get a solution within a reasonable time frame (if the input data contains a large number of flights, or the period over which we optimize is long).
Optimizing using Time Windows means that we divide the input period into smaller chunks, and we optimize over these shorter periods one after another.
Note: The smaller the time window, the further the solution will be from the optimal one, but also the faster the optimization will be.
Field | Description |
| Use Time Windows | Time windows will be used when using the column generation rotation option. The schedule will be divided into smaller periods which will be optimized one by one. |
| Use Forward Feasibility Checks | Forward Feasibility Checks will be used in the column generation optimization with time windows. Larger overlapping time windows will be solved in order to avoid infeasible solutions. |
| Use Backwards Feasibility Correction | The Column Generation algorithm moves back a time windows if the solution is infeasible in the current time window. |
| Time Window Size | From the dropdown, a selected of preset time window sizes can be chosen:
|
| Min Time Window Size | The minimum size of a time window (Given in days-hours-minutes). |
| Max Time Window Size | The maximum size a time window is allowed to be expanded to if backward feasibility correction is used (Given in days-hours-minutes). |
| Number of Forward Intervals Checks | The number of time windows that will be used in a forward feasibility check. |
Column Generation and Integer Heuristic Tab
Under this tab are internal settings for the Column Generation algorithms.

Field | Description |
| Integer Heuristic Method | The dropdown contains the different integer heuristic fixing methods:
|
| Epsilon | Relates to the aggressiveness of the fixing heuristic. A higher value of this means that more connections (or flight/vehicle pairs) will be fixed in every iteration. Should be set so that 0> epsilon<0.5. |
| Incr. Const. | This also relates to the aggressiveness of the fixing heuristic. A higher value will lead to a more aggressive behavior. Value of this should be strictly greater than one. |
| Initial Iterations | The number of iterations performed before the first time the chosen fixing heuristic is applied. |
| Iterations Before Fixing | The number of iterations performed between every time the integer fixing heuristic is applied, after the first time the fixing heuristic is applied. |
| Use Parallel Processing | Parallel processing will be used when generating new routes in the column generation algorithm. Depending on the problem, it may improve time performance.
A bit more technical answer: With parallel processing, we generate routes for each aircraft individually, and use different cores on the processor for each generation problem. Without parallel processing, we only use one core of the computers processor, but generate routes for all aircraft in the problem. We can't give a general answer other than that the "use parallel processing" option will affect the time performance, depending on how the tail assignment problem looks. |
| Use IQ Column Generation | The “integer quality column generation” algorithm will be used. This algorithm has proved to be better than the standard column generation algorithm in certain situations, particularly when a solution with no unassigned flights is hard to find. It often has a longer running time than the standard column generation algorithm. |
| IQ Column Generation Parameters | These parameters control the updating of the pseudo-dual values used in the IQ column generation algorithm. All these parameters should be strictly greater than zero:
Increasing the value of Tmax and decreasing the value of Tadd will lead to these pseudo duals being closer to the values of the true duals. |
| Labels Upper Bound/Labels Lower Bound | Both these parameters relate to the max number of “sub-routes” saved up to every flight in the generated routes. Increasing this can lead to better solutions being found, but will increase running time significantly. This parameter can be set to one if maintenance constraints are not used in the run. |
| Sink Labels Upper Bound/Sink Labels Lower Bound | Both these parameters relate to the max number of routes saved in a column generation iteration. Increasing this can lead to better solutions being found, but will increase running time. This parameter can be set to one if maintenance constraints are not used in the run. |
Objective and Penalty Functions Tab
This tab contains settings for objective and penalty functions, which are used by the ‘min cost flow’ and the ‘column generation’ algorithms, to guide the solution away from what we want to penalize, and towards what we want to achieve.
Penalty Functions
Field | Description |
| Penalize Unassigned Flights | A penalty will be used for leaving flights unassigned. It is highly recommended that this penalty is used. |
| Unassigned Flights Penalty | The penalty for leaving a flight unassigned. It is highly recommended that this is set to something high.
If all flights are not assigned to aircraft after an optimization run, this can be tried to be set to something higher. Note: When having Maintenance slots assigned to the aircraft, it sometimes happen that the optimizer leave unassigned flights. To solve this problem, use a high penalty. E.g. 100000. |
Objective Functions
This sets the goal of the optimization. Several different objective functions are implemented in the system, and they are briefly described below.
Field | Description |
| Minimize ground time between flights | Aims to minimize the ground time exceeding the minimum turnaround time for every aircraft route. |
| Robust objective function | Aims to create a robust schedule. |
| Minimize no. of unassigned flights | Aims to create a schedule where no flights are left unassigned. No optimization is performed. |
| Utilize aircraft evenly | Aims to distribute flights to aircraft as evenly as possible. |
| Crew flow from pairings, time based | Aims to make aircraft follow the pairing with the shortest connection time for every flight connection. |
| Crew flow from roster, rank based | Based on rank. For example, Captain pairings should be followed before cabin pairings. |
Legality Rules Parameters Tab
This tab contains options to use some rules in the legality system in N-OC for the Tail Assignment Optimizer. Every rule which concerns a combination of a single flight and a single aircraft can be applied. This includes the ‘Restricted station rule’, in which the user can specify certain stations as forbidden for certain aircraft. 
Note: Rules that concern something different than ‘can aircraft A fly flight B’, cannot be handled by the Tail Assignment Optimizer in its present state.
The restricted stations parameters are created in the Rules Factory.
- Dropdown contains all legality groups saved into the system.
- Selecting a group in the dropdown and clicking ‘Show Rules’ displays the rules in this group in the left window.
- You can here select one or multiple rules and move them over to ‘Rules To Use’, which will make the tail assignment optimizer consider these rules during a run, in that the solution it provides will not violate them.
Buttons | Descriptions |
 | Moves over every rule in the ’Available Rules’ window to the ’Rules To Use’ window. |
 | Moves over every highlighted rule in ’Available Rules’ to ’Rules To Use’. |
 | Moves over every highlighted rule in ’Rules To Use’ to ’Available Rules’. |
 | Moves over every rule in ’Rules To Use’ to ’Available Rules’. |
Maintenance Tab
The Maintenance options in the Tail Assignment Optimizer works as such as the user defines maintenance checks which the aircraft must undergo. It is then specified on which stations and at what times these maintenance checks can be performed.
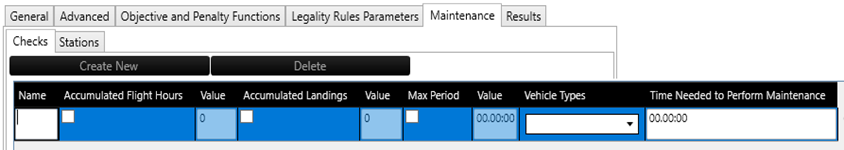
Checks Tab
In this tab, you can create maintenance checks which need to be performed on the aircraft. Rules can be set up such that there is a limit on the maximum flight hours, the maximum number of landings, and the maximum time between two succeeding maintenance checks. You can also specify here for which aircraft types the check applies, and how long the maintenance check takes to perform.
To create a new maintenance check, click the Create New button. As can be seen in the figure, a new line appears where the different maintenance options for this newly created maintenance check can be entered. To delete the highlighted maintenance check, click the Delete button.
Field | Description |
| Name | Name of the maintenance check. |
| Accumulated Flight Hours | A rule will be used for the maximum flight hours before this maintenance check is performed |
| Value | The maximum flight hours before this check must be performed. |
| Accumulated Landings | A rule will be used for the maximum number of landings before this maintenance check is performed. |
| Value | The maximum number of landings before this maintenance check is performed. |
| Max Period | A rule will be used for the maximum time allowed to pass before this maintenance check is performed. |
| Value | The maximum time allowed to pass before this maintenance check is performed. |
| Vehicle Types | The vehicle types for which this maintenance check applies. |
| Time Needed to Perform Maintenance | The time this maintenance check takes to perform. |
Stations Tab
In this tab, rules for each station can be set. For each station, you can specify the opening times during which maintenance can be performed, and also specify which particular maintenance checks can be performed.
To create a rule for a specific airport, select that airport in the dropdown then fill in the options on the right side panel.
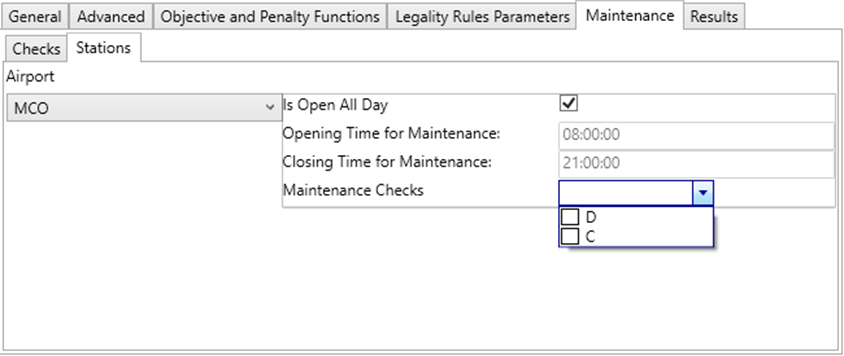
Field | Description |
| Is Open All Day | If checked, maintenance can be performed on this airport every hour of the day. If unchecked, maintenance can only be performed in the hours between ‘Opening Time for Maintenance’ and ‘Closing Time for Maintenance’. |
| Opening Time for Maintenance | The starting time of the day at which maintenance can be performed. |
| Closing Time for Maintenance | The stop time of the day, at which maintenance can no longer be performed. |
| Maintenance Checks | The maintenance checks which can be performed at the selected airport. Note: The checks come from the checks grid. |
Results Tab
Under this tab, results from a successful run will be displayed. Under ‘General result’, results regarding the overall solution are shown. Under ‘Aircraft Result’, results regarding individual vehicles are displayed.
General Advice
- Different settings apply to different rotation options (or algorithms). For LIFO and FIFO, the parameters “Ignore onward”, “Ignore type”, “Ignore version”, “Ignore initial positions”, “Use estimated times”, “Ignore multileg connections”, and “Use fixed turn around time” will influence the solution.
- For Minimum cost flow, in addition to the parameters affecting the solution from LIFO/FIFO, the “objective function” and the “penalty for unassigned flights” will also affect the solution.
- For column generation, all parameter setting will affect the solution.
- If onward references exist for all flights, and you just want a solution which follows these references, it is sufficient to choose one of the faster Rotation Options (LIFO/FIFO/Min cost flow), and to uncheck ‘Ignore Onward’.
- After a successful run, the solution will be displayed in the Schedule Gantt, but will be saved first after the ‘Save’ button in the tail assignment wizard is checked.


